a6046245-04ae-401a-a229-1bd0321718d1.jpg?sfvrsn=ee874d96_0)

Colorectal cancer is a disease affecting the colon and rectum in which cells in either organ grow out of control. Sometimes it is called colon cancer, for short.
Colorectal cancer is the most prevalent cancer in Malaysian men (affecting about 15 in 100,000 people) and the second most common cancer in Malaysian women (affecting 11.1 in 100,000 people). It is also Malaysia's third leading cause of cancer deaths.
Causes of colorectal (colon) cancer
There are several factors involved but the ultimate changes occur in the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of our cells. DNA changes or mutations can cause cells to grow out of control and the expression or suppression of certain genes can lead to tumour formation.
Risk factors of colorectal (colon) cancer
Signs and symptoms of colorectal (colon) cancer
Early-stage colorectal cancer is likely to be symptom-free and can be identified through active screening for colorectal cancer.
Some signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer are:
Diagnosis of colorectal (colon) cancer
Learn more about the different types of screening and diagnostic procedures performed to diagnose colorectal (colon) cancer.
Treatment options for colorectal (colon) cancer
Learn more about the different types of treatment technologies to treat colorectal (colon) cancer.
Prevention of colorectal (colon) cancer
You can help prevent colorectal cancer by practising the following healthy habits:
Detect to Protect!
It is recommended that individuals with an average risk of colon cancer begin colon cancer screening around the age of 45. However, people who are at a higher risk e.g. those who have a family history of colon cancer, should consider screening earlier.
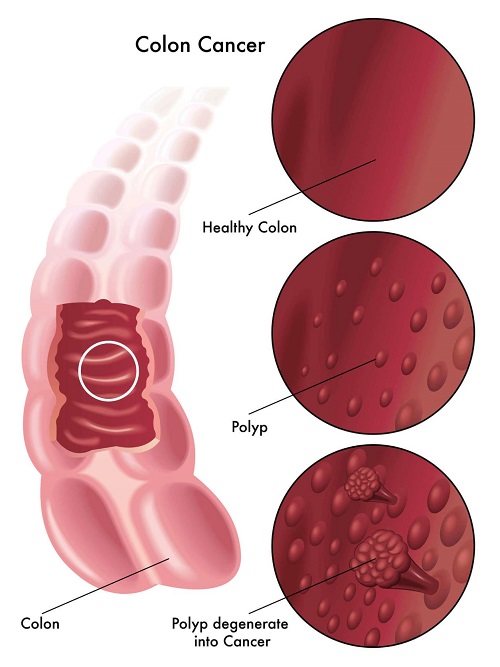
Screening tests can detect precancerous polyps, allowing them to be removed before they develop into cancer. Colorectal cancer screening tests can also detect the cancer early, when therapy is most effective.
Screening methods for colorectal (colon) cancer
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a very effective procedure in screening, diagnosing and preventing colorectal cancer. The procedure is performed under sedation and involves the doctor examining the entire colon.
If precancerous polyps are found, they can be removed during the colonoscopy thus preventing them from developing into cancer.
Immunochemical faecal occult blood test (iFOBT)
Immunochemical faecal occult blood test (iFOBT) is a lab test that can identify blood in stool that are not seen by the naked eye. The stool is collected at home and sent to a lab. Individuals above the age of 50 are encouraged to do iFOBT once a year.
Make an appointment at Gleneagles Hospitals
If you notice any changes in your bowel behaviour or if you have any of the symptoms of colorectal (colon) cancer, get in touch with us to find out more about our Oncology Services at your nearest Gleneagles Hospital.
Gleneagles Hospital works with oncologists to assist patients through cancer treatment. The caring and multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals are available for consultation and to provide the best care.

Wait a minute

Wait a minute