This Might Interest You

The prostate is a key part of the male reproductive system and can sometimes cause discomfort and embarrassment. Many men avoid discussing prostate issues due to their sensitive nature. Dr. Han Pei Kw...
.webp?sfvrsn=cac9ca10_7)
At Gleneagles Hospital Johor, we are proud to embrace the latest advancements in medical technology to provide our patients with the best care possible. One of the most exciting developments in the fi...

In the hustle of modern work life, spine health often takes a backseat as we silently endure the demands of office jobs. Dr. Mohd Zaim Mohd Rashid, a consultant in Orthopaedic & Spinal Surgery at ...

Do you think that persistent coughing, a raspy voice, and wheezing are just signs of a cold? If you start coughing up blood, experiencing chest pain, or rapidly losing weight, you might already be in ...

As men age, so does their prostate.An enlarged prostate could cause various issues such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a relatively common condition faced by older men.
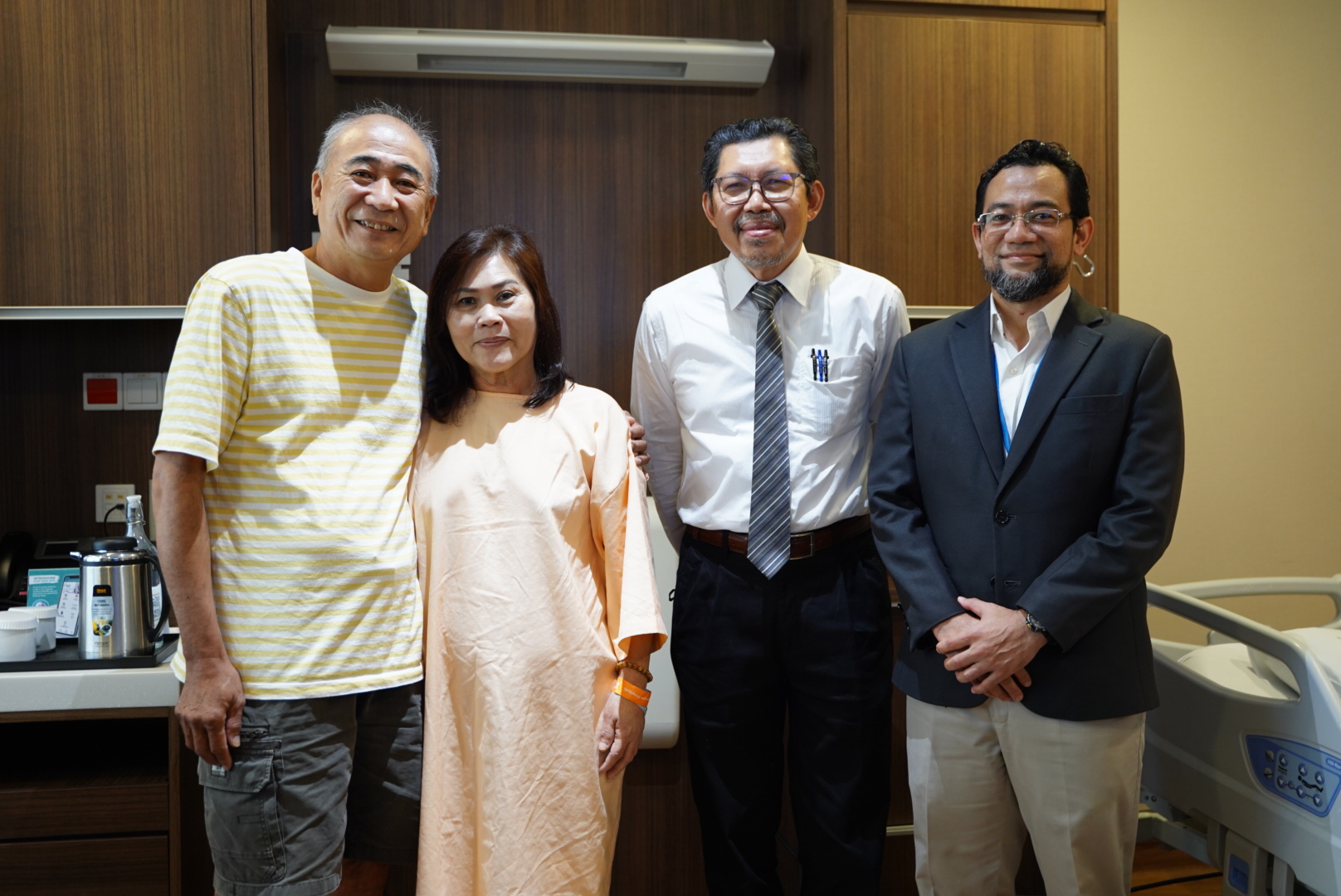

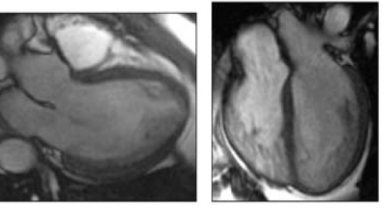
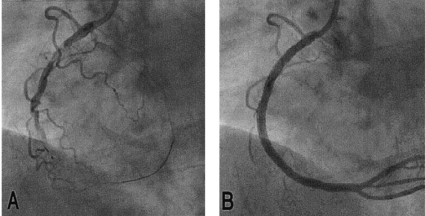
That’s right, the heart was still beating during the bypass surgery. (Conventional bypass would neccesitate the cessation of heart function during surgery).



403e3657-220f-45bf-9e5b-ac105118fdbe.png?Status=Master&sfvrsn=41942b98_6)