Everyone has heard of a heart attack, but far fewer people are familiar with pulmonary embolism—a serious medical condition that affects thousands of people each year and requires immediate medical attention.
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot (typically forming in the deep veins of the legs) breaks loose, travels through the bloodstream, and becomes lodged in the blood vessels of the lungs. This blockage:
In severe cases, PE places extreme strain on the heart, potentially leading to heart failure.
A comprehensive study published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis found that PE is the third most common cause of cardiovascular death worldwide, after heart attacks and strokes. [1]
PE symptoms can vary widely depending on the size of the clot and how much of the lung is affected. Be alert for:
What makes PE particularly dangerous is that its symptoms can mimic other conditions, potentially delaying diagnosis. Some people experience only mild symptoms, while others may suddenly collapse.
Research published indicates that up to 30% of PE cases are initially misdiagnosed, highlighting the importance of increased awareness among both the public and healthcare providers. [2]
Several factors can increase your likelihood of developing blood clots that might lead to PE:
According to medical statistics, untreated PE has a mortality rate of approximately 30%, making rapid diagnosis and treatment essential.
For severe PE cases, mechanical thrombectomy has emerged as a game-changing intervention. Unlike traditional treatments that rely on medications to dissolve clots over time, mechanical thrombectomy physically removes the clot from the pulmonary arteries.
Benefits include:
The FLARE study, published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, demonstrated that patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy showed significant clinical improvement within 48 hours of the procedure. [3]
The FlowTriever System is the first FDA 510(k)-cleared mechanical thrombectomy system designed specifically for treating PE. Engineered for rapid blood clot removal and immediate symptom relief, it offers a ground-breaking, minimally invasive solution for patients with acute PE.
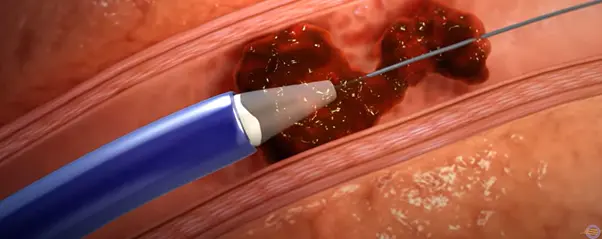

(Image 1: The FlowTriever catheter is designed to mechanically engage, disrupt, and remove blood clots.)
At Gleneagles Hospital Penang, we are proud to be the first private hospital in Malaysia with expertise from our consultants, Dr Neoh Eu Rick and Dr Rajesh P. Shah to introduce this cutting-edge technology, reaffirming our commitment to advanced, patient-centred care.
If you experience sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or other concerning symptoms—especially if you have risk factors for blood clots—seek medical attention immediately.
When it comes to pulmonary embolism, early intervention can make all the difference between life and death.
For more information, visit our cardiologists at Gleneagles Hospital Penang.

Wait a minute

Wait a minute