According to the American Cardiac Association studies, 9 out of every 1000 newborns have congenital heart defects.
Data obtained from the Global Burden of Disease study from 2017 revealed that congenital heart defect is more common in developing nations and less common in developed nations. Heart problems are typically present in 0.8 % to 1.2 % of live births worldwide.
Understanding CHD
Congenital is an adjective used to describe something that exists from birth. Therefore, congenital heart disease describes a heart abnormality, which is present from birth that interferes with how a heart normally functions.
It could manifest as a structural or functional anomaly in a baby's heart that could impair the body's overall blood flow.
Types of congenital heart defects
There are generally three different types of congenital heart defects:
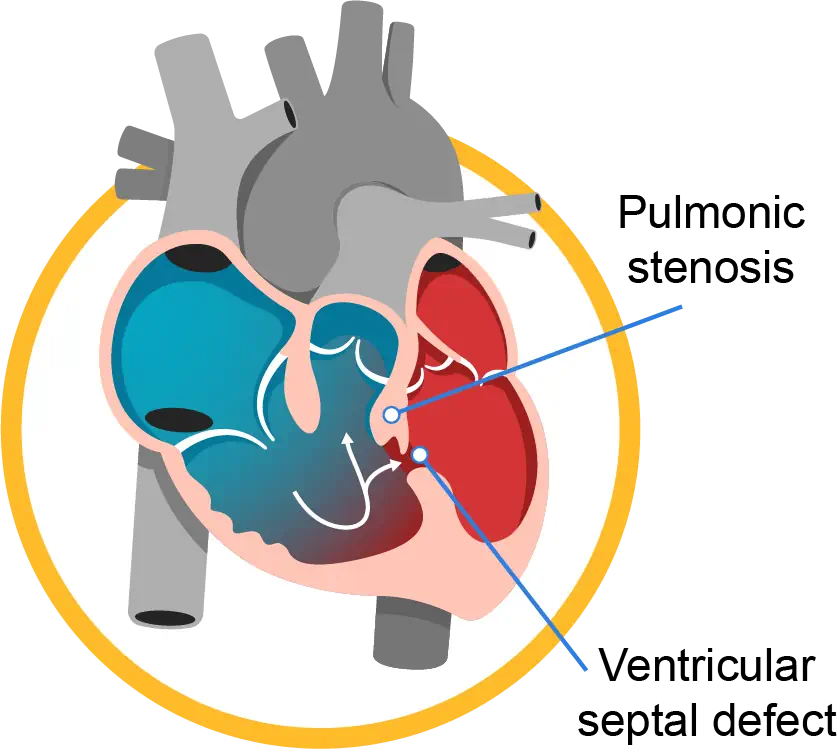
Heart valve defects - These occur when a heart valve becomes too narrow (e.g., aortic coarctation) or closes (e.g., bicuspid aorta). This causes an inability of the heart to pump blood correctly. In certain cases, the valve cannot close completely, enabling the blood to flow backward (e.g., aortic regurgitation).
Heart wall defects - The left and right heart chambers are divided by a natural wall. A defect would affect the development of the wall, resulting in the mixing of pure and impure blood. It might also result in blood flowing back into the heart or accumulating in other parts of the body where it isn't supposed to. As a result, the heart would have to work harder, causing the blood pressure to rise.
Blood vessel defects - When this occurs, the blood vessels that transport blood to and from the heart may not operate effectively, resulting in a number of heart issues.
Common congenital heart defects
Causes
The heart of a foetus develops during the initial eight weeks of pregnancy. If the foetus has a defect, it typically manifests itself at this critical period.
There are several causes of congenital heart defects in infants.
One cause is the alterations in the chromosomes and genes of the infant. This may be hereditary and may be inherited from either parent. The genetic condition that is most well-known and can result in a defect is Down's syndrome. Turner and Noonan's syndrome are other genetic conditions that are associated with congenital heart defects.

Risk factors
Babies may develop heart defects if the mother uses certain medications.
For instance, the use of benzodiazepines or ibuprofen is associated with a higher risk of a baby being born with a heart abnormality.
Additionally, contracting the flu during the first trimester may increase the risk of congenital heart abnormalities. Therefore, it is advised that all women get vaccinated before getting pregnant.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms in adults
Symptoms in children
It is possible for newborns with heart problems to have blue skin, lips, fingers and toes. They might struggle to breathe or feed, breathe quickly, have an irregular heartbeat or have a very low birth weight.
Congenital heart symptoms can sometimes go unnoticed until a few years after birth. However, once they occur, you may experience symptoms such as excessive exhaustion, dizziness, or swelling in your hands, feet, ankles, or legs.
Diagnosis
Foetal echocardiography, which produces ultrasound images of the developing baby's heart, can be used to diagnose some congenital heart defects during pregnancy. Additionally, your doctor may also perform a few physical examinations.
Here are some tests that might be used in the diagnosis of a heart defect in adults or newborns:
Treatment options
The advanced medical technology and high standards of medical science currently available make it possible to correct most congenital cardiac problems, if not all of them, if discovered early.
The type of treatment is determined by how severe the defect is. Among the treatment options available are:
Life expectancy for CHD
The survival rate of newborns with congenital cardiac disease depends on the severity of the defect, when the defect was discovered and how the defect is treated.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that 97% of infants born with non-critical heart problems will survive to be a year old, and 95% will survive up to the age of 18.
It is predicted that 75% of infants with critical heart conditions will survive their first year and 69% will do so until they are 18 years old.
Prevention
Given that the exact causes of congenital heart defects are unknown, prevention may not be possible. However, here are some measures you can take to help lower the risk:
Visit your nearest Gleneagles Hospital to learn more about our Cardiology Services
References:

Wait a minute