The human bones have sufficient strength and resilience to withstand a significant amount of stress.
When we talk about a fracture, it refers to a broken bone, whereby the bone may be partially or completely cracked or broken.
A fracture can occur due to the following situations:
- Injuries suchas a sudden or excessive force that may be direct or indirect. This is usually due to a fall or an accident.
- Repetitive stress, meaning repeated heavy loading, such as in athletes or dancers.
- For people who have conditions such as osteoporosis or osteogenesis imperfecta, they may have pathological fracture or an abnormal weakening of the bone.

Classifications of fractures
Fractures can be classified into:
- Open fracture (compound fracture): The bone pierces through the skin and is visible, or a deep wound exposes the bone through the skin.
- Closed fracture (simple fracture): The skin is intact, but the bone is broken.
Common types of fractures
Types of fracture | Description |
|---|
Transverse fracture 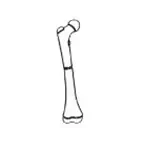 | Horizontal fracture line. |
Oblique fracture  | The bone is broken diagonally. |
Spiral fracture 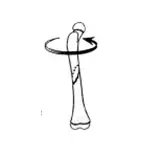 | The fracture spirals around the bone. Commonly seen in twisting injuries. |
Comminuted fracture 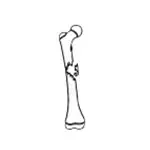 | There are more than two fracture fragments. |
Segmental fracture 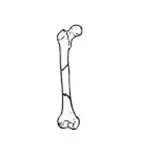 | At least two fracture lines that together isolate a bone segment. |
Greenstick fracture 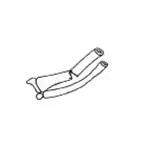 | Incomplete fracture accompanied by angular deformity (like snapping a green twig). Seen in children. |
Impacted fracture 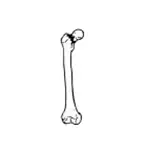 | Fracture due to impact on adjacent bone. |
Compression fracture  | A type of fracture that causes the vertebrae to collapse. |
Stress fracture | A small crack or severe bruise within a bone caused by repetitive trauma. |
Fracture symptoms
- Intense pain
- Swelling, bruising or tenderness at the injury site
- Deformity of the limb
- Inability to move the injured limb
- Numbness and tingling sensation
Fracture diagnosis
Patients with suspected fractures
- Patients with suspected fractures need prompt and, oftentimes, emergency evaluation to determine the presence of potentially life-threatening complications.
- Following a major trauma or significant injury, patients should go to the Emergency Department for a comprehensive evaluation immediately.
Patients without life-threatening injuries
- Patients without life-threatening injuries can be assessed at the Orthopaedic clinic. Your doctor would first question your general health and symptoms before conducting a thorough physical examination. Diagnosis is made based on your reported symptoms, physical examination, and investigations.
- Your doctor would request an x-ray to verify the diagnosis and determine the exact location of the fracture in the bone. When the full extent of a fracture is not apparent on an x-ray, computed tomography (CT) scan may be requested for accurate visualisation of the fracture.
Fracture treatment options
- Non-surgical treatment options
- A closed reduction may be required if the fracture is significantly displaced.
- Immobilisation thatinvolves the usage of a splint, cast or brace will be necessary to keep the bone in place and prevent further injury.
- Adequate analgesia is required for effective pain management. Minor fractures may be treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), whereas severe pain may require a combination of NSAIDs and short-acting opioids.
- Surgical treatment options
- External fixation: A device (external fixator) is used to hold the fracture in a steel frame outside the limb. Pins are passed through to hold the bone and are connected to the bar outside. It is useful for open fractures as internal fixators cannot be used due to infection.
- Internal fixation: After reduction, the fracture is internally held with metallic or non-metallic devices such as screws, plates, Kirschner (K-wire) or intramedullary nail.
The healing time for a fracture can range from several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury, patient’s age, how well does the patient follow their doctor's instructions, and other factors that influence fracture healing.
Make an appointment at Gleneagles Hospitals
Speak to your doctor to know more about the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for orthopaedic conditions. The caring and multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals are available for consultation and to provide the best care.
Get in touch with us to book an appointment with an Orthopaedic specialist at Gleneagles Hospital today.
If you encounter a situation that requires medical attention, please seek immediate medical attention at the Accident and Emergency (A&E) department at your nearest Gleneagles Hospital.









