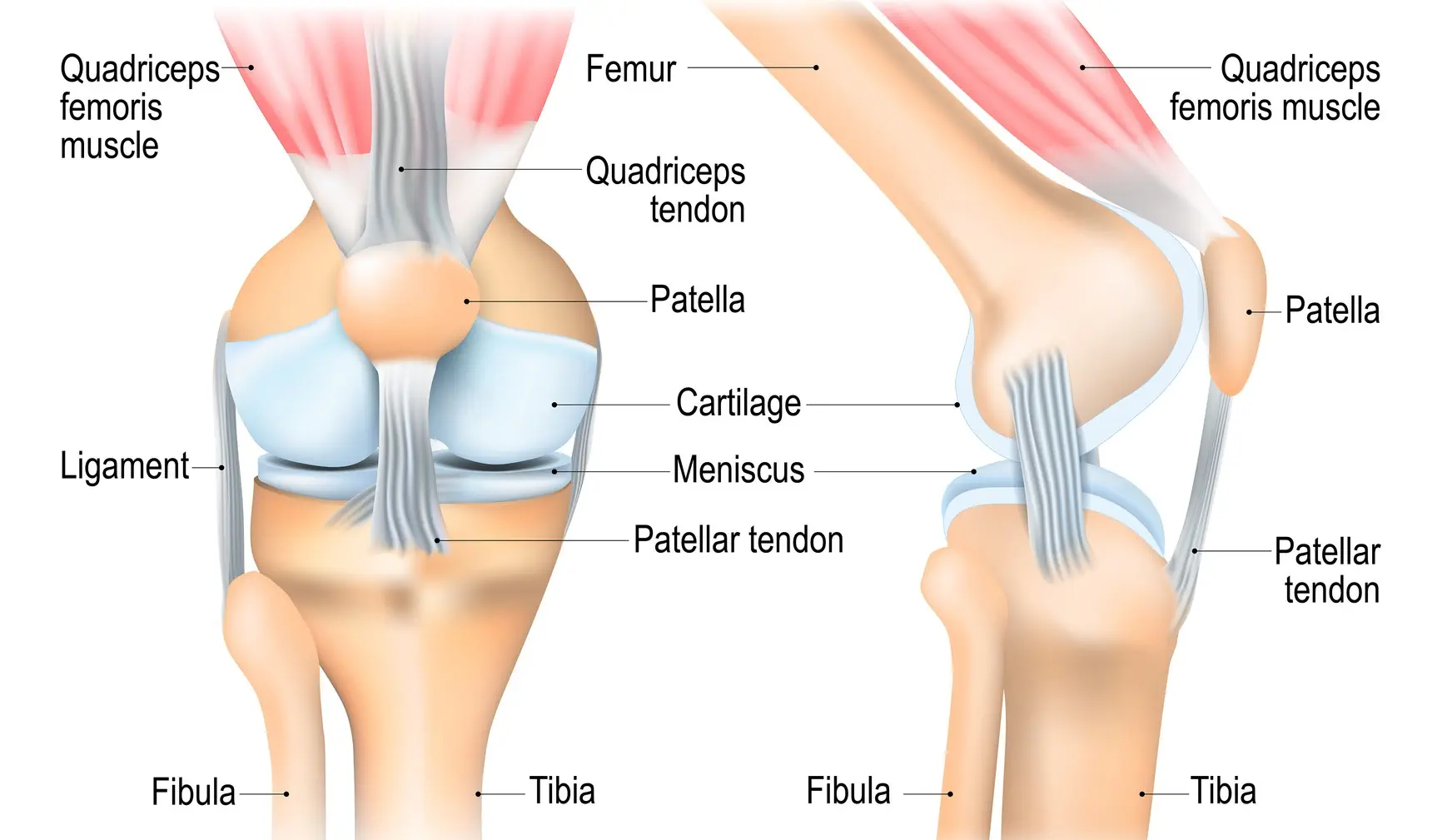
In the human knee, the cartilage is a tough and rubbery tissue that cushions the joints. As the knee joint moves, the cartilage cushions the bones, enabling them to glide against one another without friction.
However, the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap (patella) can soften and break down due to overuse or injury. This condition is known as chondromalacia patella. As the knee joint moves, the worn-out cartilage is unable to protect the ends of the bones, thus leading to friction of the bones, causing pain.

Chondromalacia Patella symptoms
Chondromalacia Patella risk factors
Chondromalacia Patella diagnosis
Your doctor would first question your general health and symptoms before conducting a thorough physical examination.
Diagnosis is made based on your reported symptoms, physical examination, and investigations.
Chondromalacia Patella treatment
Non-surgical treatments can alleviate knee pain for most people with chondromalacia patella.
Surgical treatment
Your doctor may recommend surgery (arthroscopy) if symptoms persist despite conservative treatment. During arthroscopy, the damaged layers of the cartilage can be removed. The alignment of your kneecap or other parts of your knee can be corrected to reduce wear and tear on your knee cartilage.
Chondromalacia Patella prevention
You can reduce the risk of developing chondromalacia patella by preventing knee injuries and joint overuse.
Make an appointment at Gleneagles Hospitals
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of chondromalacia patella, get in touch with us to find out more about ourOrthopaedic Servicesat your nearest Gleneagles Hospital.
Gleneagles Hospital works with orthopaedic specialists to assist patients through diagnosis and treatment. The caring and multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals are available for consultation and to provide the best care.

Wait a minute