Pathogenic microorganisms (pathogens) such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi can cause infectious diseases, in which the contagious diseases spread directly or indirectly from one person to another.
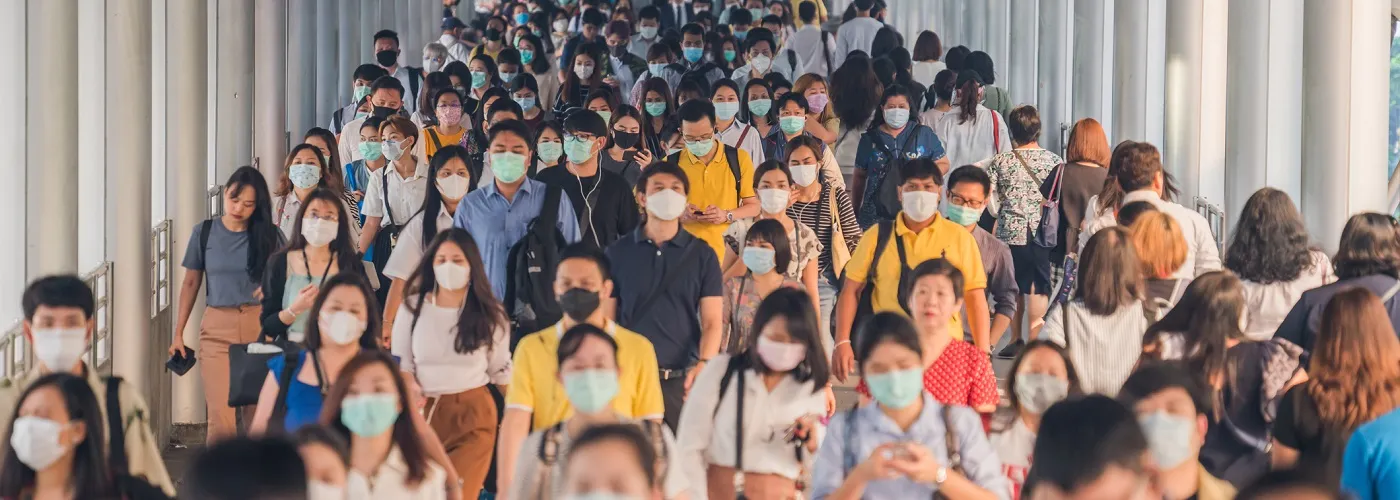

There are many ways that infectious diseases spread.
Small respiratory droplets containing germs (for example, flu virus) are released into the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets may linger in the air and breathed in by people whom they are talking to.
Touching your mouth, eyes, and nose (without washing hands that are contaminated by droplets) may also get you infected.
Infection can spread via direct skin or mucous membrane contact with an infected person. Mucous membrane is the moist lining in a person’s nose, mouth, throat, and genitals.
Infection can also spread when blood or bodily fluids such as saliva, semen, vaginal secretions of an infected person come into contact with another person when they are kissing or engaged in sexual activities (sexual contact).
Infection can happen when utensils and personal belongings of an infected person are being shared with other people.
Germs can also be passed indirectly if they are present on objects such as doorknobs, utensils, tabletops, etc. Touching these surfaces and then touching your mouth, eyes, and nose (without washing hands) may get you infected.
Some infectious diseases spread when germs enter the human body through food and water contaminated by stool (faeces) particles from an infected person.
Certain infections rely on insect carriers (usually mosquitoes) that carry pathogens such as malaria, dengue virus, and Zika virus to get transferred from one host to another. Such carriers are called vectors.
There are certain risk factors that increase the risks of someone getting an infectious disease.
Signs and symptoms of an infectious disease depend on the organism causing the infection, but fever and fatigue are the most common signs and symptoms of infectious diseases. In addition, other general signs and symptoms include diarrhoea, muscle aches, and coughing.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you:
Infectious diseases usually resolve without serious complications if medical attention is sought early.
However, certain infections such as AIDS, meningitis, and pneumonia can become life- threatening.
There are also certain infections that have been linked to long term complications and serious diseases:
Treatment of infectious diseases depends on the microorganism that caused the infection.
Your doctor will assess your symptoms and decide on the course of treatment accordingly.
To minimise your risk of infection, you are advised to have good personal hygiene, for example, wash your hands before eating and after using the toilet.
Avoid sharing personal items like toothbrush, comb, razor, towel, drinking glasses and dining utensils.
In addition, get vaccinated and practice safe sex can also reduce your chance of contracting many diseases.

Wait a minute