What Is A Pleuroscopy Or Medical Thoracoscopy?
Pleuroscopy is an examination of the space between the lung and the chest wall, where a thin tube called a pleuroscope is inserted through the skin on the chest into the pleural space (space between the lung and ribs). This procedure is carried out to investigate the cause of fluid (Image 1) or air in the pleural space.
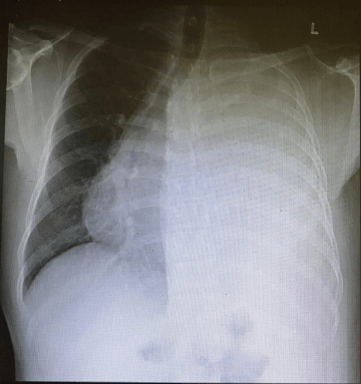
Image 1: Pleural effusion – the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space, seen on the left chest
How Is It Done?
You will lie on your side during the procedure and have a rolled-up towel placed beneath you.
You may receive a sedative drug for relaxation. Your doctor will inject a local anaesthesia into the muscle between your ribs.
He / she will then make a small cut in the skin and place a hollow tube though the cut into the pleural space. Sometimes, a second cut may be needed.
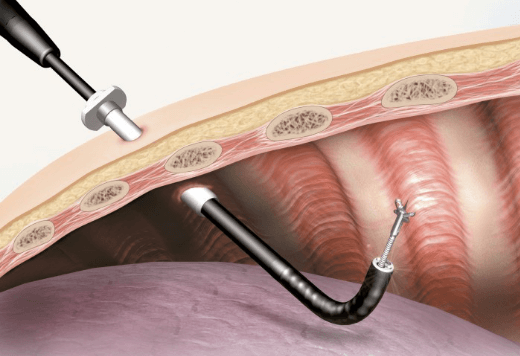
A telescopic instrument is introduced through the hollow tube. Your doctor will use this instrument to scan the pleural space.
He / she may obtain pleural biopsies by removing small pieces of the lining of the pleural space. This may cause some pain. Pain relief may be given before the biopsy.
The fluid in the pleural space will be drained. This procedure does not stop your normal breathing.
At the end of the procedure, a chest tube will be inserted into the incision to drain any air or fluid from your pleural space.
Local Anaesthesia and Sedation:
This procedure will require anaesthesia. Information about anaesthesia and its risks involved will be discussed before the procedure. If you have any concerns, discuss these with your doctor.
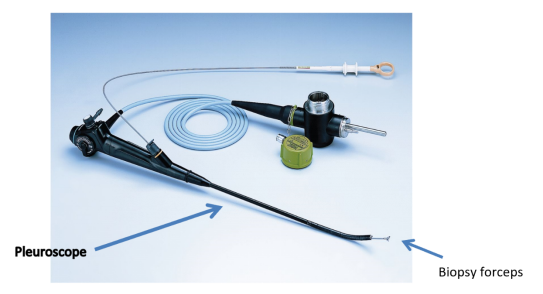
Image 2: A Pleuroscopy Set
(source:https://breathe.ersjournals.com/content/8/2/156.figures-only)
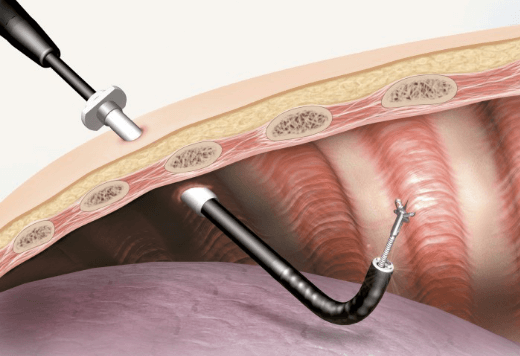
Image 3: Pleuroscopy in the pleural space
(source:https://ssd.olympus.eu/medical/en/medical_systems/applications/pulmonology/medical_thoracoscopy/medical_thoracoscopy_1.html)
What Are The Risks Of Getting A Pleuroscopy?
Before the procedure:
After the procedure:

Wait a minute

Wait a minute