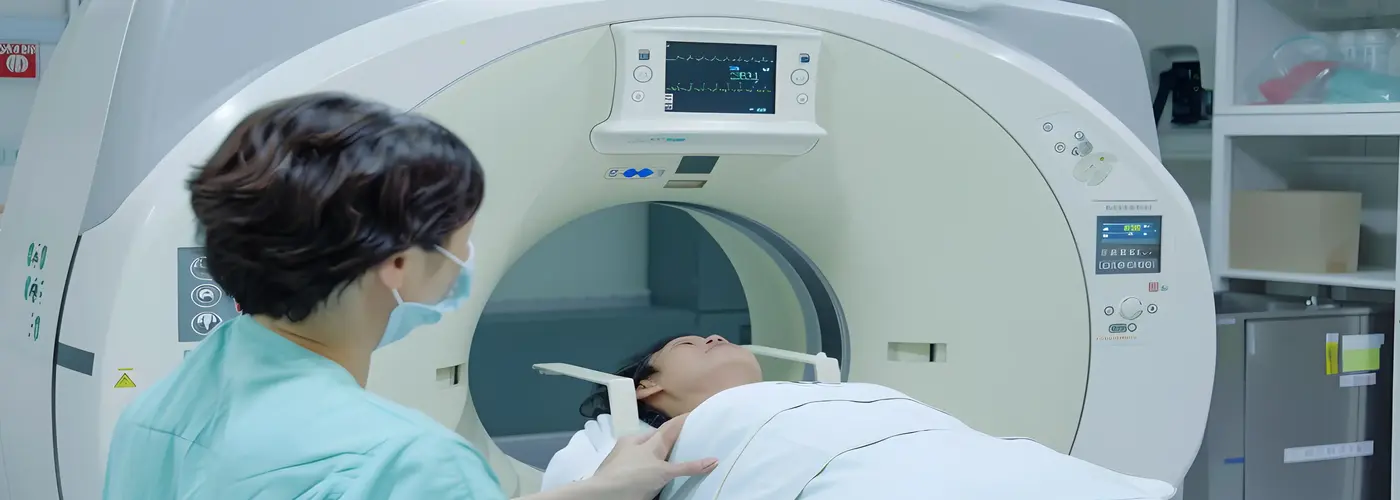
A CT scan (Computed Tomography) is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. These images, known as "slices," provide a clear view of internal organs, bones, and soft tissues, helping doctors diagnose, and monitor various conditions.
The scan is non-invasive and relatively simple, where you lie on a table that moves through a ring-shaped scanner. As the X-ray source rotates around your body, it produces multiple images that are stacked together into a 3D view, offering a more comprehensive analysis.
CT scans are used to detect a wide range of conditions, including tumors, internal injuries, blood clots, and other medical issues. They are invaluable tools for doctors in planning treatments and monitoring ongoing health concerns.
Before the procedure, some preparation is required. Fasting for at least four hours is necessary, especially if an intravenous contrast injection is needed. It’s important to inform the staff of any allergies or current medications you are taking, as this may affect the procedure or results. The results from a CT scan give doctors crucial insights to help in diagnosing your condition.
A CT scan is a highly effective diagnostic tool that provides detailed views of various tissues, including the lungs, bones, soft tissues, and blood vessels. If you suffered a stroke, a CT scan can determine the location of the blockage or bleeding in the brain that has caused the stroke, allowing doctors to make informed decisions about your treatment.
In addition to its role in diagnosing conditions like strokes, a CT scan is essential in identifying both normal and abnormal structures in the body. It does this in a painless, non-invasive, and highly accurate manner, providing doctors with crucial insights into your health.
Computerised tomography is also a valuable tool for planning and preparing for certain surgeries including awake craniotomy (brain surgery to remove brain lesions) and deep brain stimulation surgery. It is also useful in the planning and guiding of radiotherapy (cancer treatment), needle biopsies, and other minimally invasive operations.
In Malaysia, the CT scan technology is widely used in hospitals and medical centers for both diagnostic and procedural guidance, ensuring that patients receive the most accurate and efficient care possible.
Preparation for your CT scan may vary based on the procedure. The radiologist will provide specific instructions, but generally, you may need to:
Make sure to inform the doctor if you:
By following these guidelines, you can help ensure a smooth CT scan experience.
A CT scan typically lasts 10 to 20 minutes and is performed by a radiographer in a hospital. Before the scan, you may receive a contrast medium (dye) to help highlight certain areas in the images. This can be administered orally, via injection, or through the rectum. If injected, you may feel hot, flushed, or experience a metallic taste in your mouth, these sensations usually pass quickly.
During the scan, you'll lie on a flat bed as the CT scanner, a large ring-shaped machine, moves around your body. The radiographer, who operates the scanner from another room, will ask you to remain still and may ask you to hold your breath at times to ensure clear images.
After the CT scan, if you received a contrast medium, you may need to wait for up to 30 minutes to monitor for any reactions. If you're an outpatient, you can leave the hospital shortly afterward.
It typically takes 1 to 2 weeks to receive your CT scan results, though it can take up to 4 weeks depending on urgency and your location. A radiology specialist will review the images and send the findings to your referring doctor.
You may need a follow-up appointment to discuss the results. If you haven’t heard anything after 4 weeks, contact the doctor who referred you. They will explain the results and discuss the next steps, which may include additional tests, depending on the reason for your CT scan.
If you have any questions or don’t understand your results, don’t hesitate to speak with a healthcare professional.
Complications from a CT scan are very rare. If you received a contrast dye, you may be asked to wait for a short time after the scan to ensure you don’t have an allergic reaction. If you feel unwell, let the radiographer know right away.
While the risk is minimal, repeated CT scans do involve exposure to a small amount of radiation. Your doctor will carefully weigh the benefits and risks and will discuss any concerns with you before proceeding.
At Gleneagles Hospitals, we prioritise your safety and well-being during every procedure, including CT scans. Rest assured, our team takes every measure to ensure that you receive the best care while minimising any risks. If you have any concerns or questions, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We’re here to help you through every step of your healthcare journey.

Wait a minute