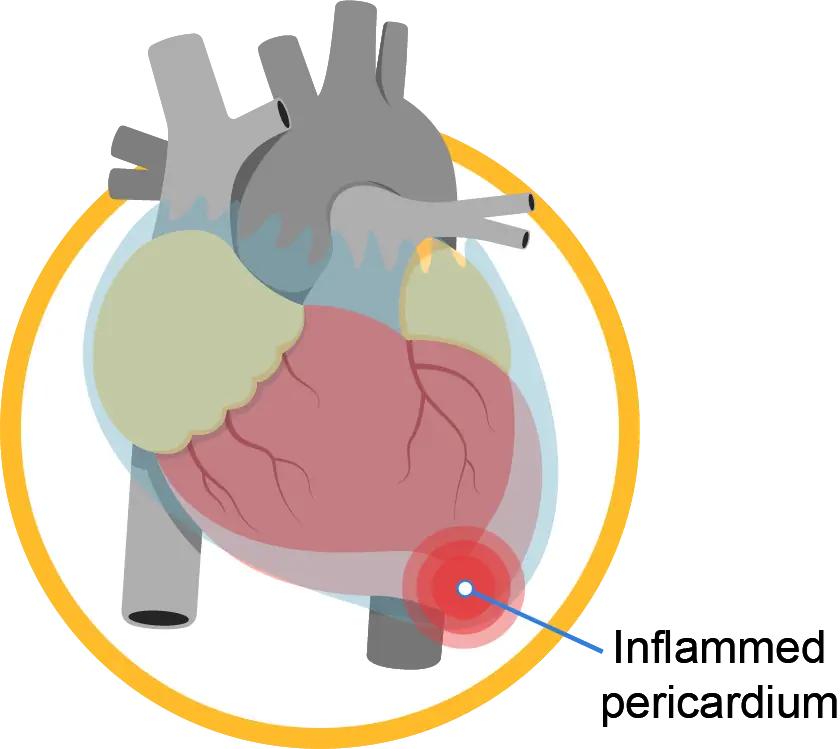
The pericardium is a thin fibrous sac that encircles and envelops the heart while providing it structural support.
Acute pericarditis, pericardial tamponade, and pericardial constriction are some of the most significant pericardial diseases.
Causes
Acute pericarditis | Cardiac tamponade | Pericardial constriction |
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms
Acute pericarditis | Cardiac tamponade | Pericardial constriction |
|
|
|
Diagnosis
Acute pericarditis | Cardiac tamponade | Pericardial constriction |
|
|
|
Treatment options
Acute pericarditis | Cardiac tamponade | Pericardial constriction |
|
|
|
Prevention
While pericardial diseases such as acute pericarditis and cardiac tamponade cannot be prevented, measures can be taken to reduce your risk of experiencing another acute episode or complication. These include:
Visit your nearest Gleneagles Hospital to learn more about our Cardiology Services
References:

Wait a minute