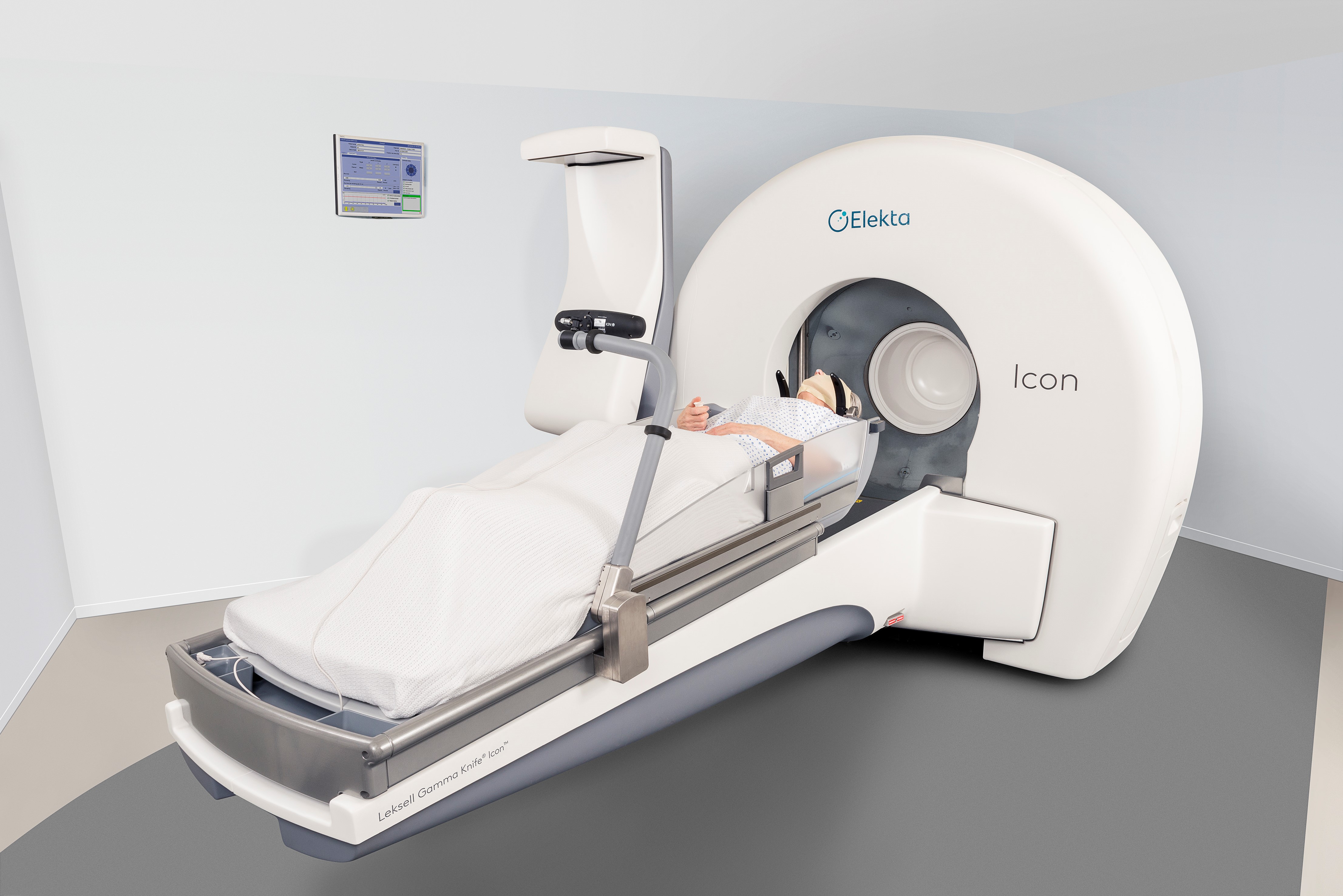
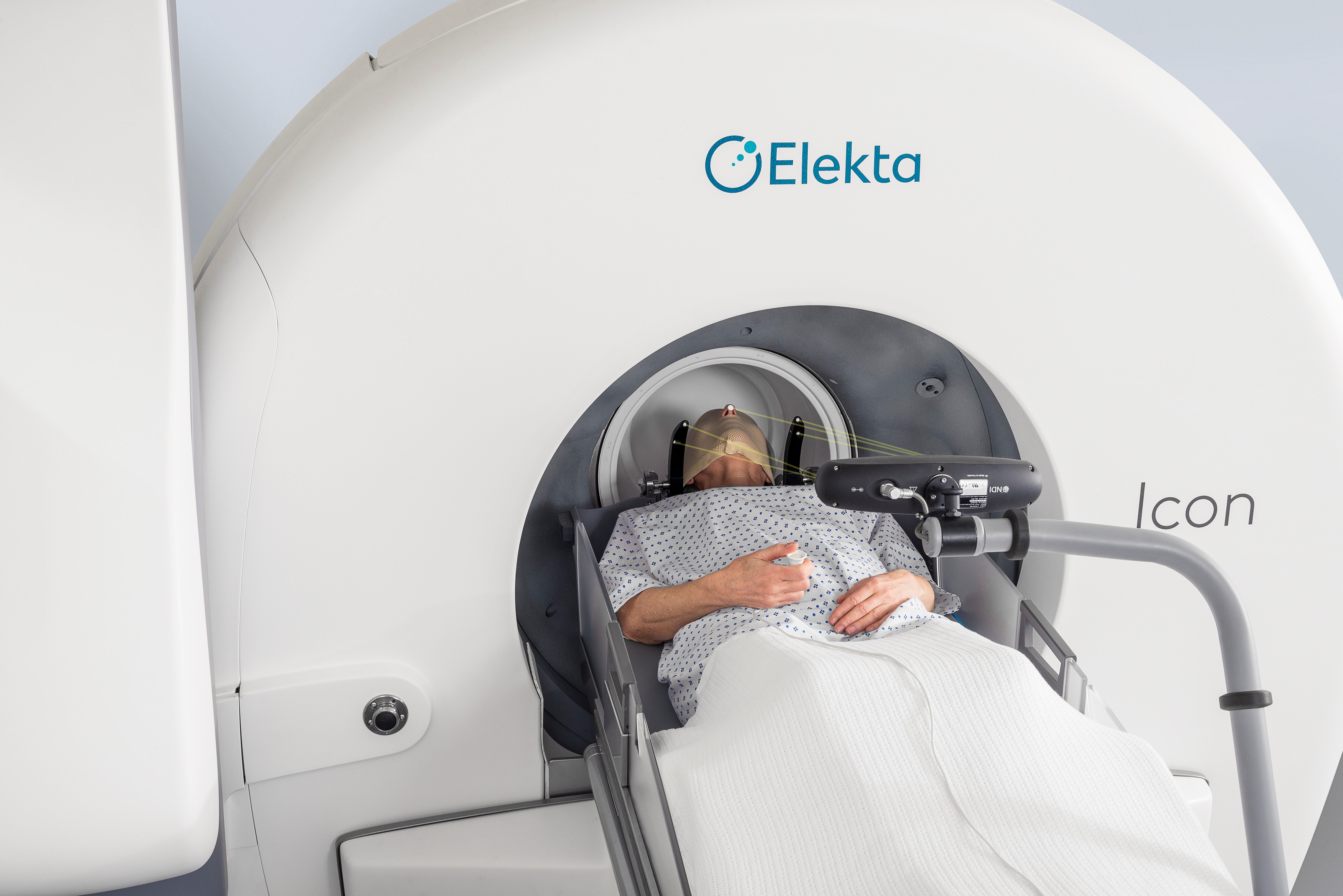
Gamma Knife procedure (GK) has become an increasingly popular method for treating many brain diseases. Also known as Gamma Knife radiosurgery or stereotactic radiosurgery, GK is progressively being applied in patients with various brain diseases.
It is also commonly used to treat metastases which are tumours that have spread from other parts of the body to the brain. Gamma Knife is also effective in the treatment of vascular lesions such as arterio-venous malformations and cavernomas.
Additionally, GK can be used to treat pain as in trigeminal neuralgia and glossopharyngeal neuralgia, and movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy and obsessive-compulsive disorders.
Gamma radiation from a Cobalt 60 source is used in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
According to Gleneagles Hospital Kuala Lumpur consultant neurosurgeon Dato' Dr Jagdeep Singh Nanra, GK is a highly accurate radiosurgery procedure that is usually performed with the application of a stereotactic frame.
“GK uses many beams of Cobalt 60 radiation from multiple angles to target one specific area in the brain. There are 192 sources of radiation targeting to a point,” he added.
"GK can be used as a primary treatment in many brain diseases or as an adjunct to surgery. In general, if a condition is ideal for GK, the associated risks are significantly less," Dato' Dr Jagdeep explained. In most cases, GK could be a one-time therapy completed in a single day to treat the patient’s condition.
"This would depend on many factors, mainly the size of the tumour, location and the proximity of organs at risk. If the size of the tumour is not more than 3-3.5cm, a single session treatment will suffice," Dato' Dr Jagdeep explained.

Gamma Knife radiosurgery is commonly used to treat benign or malignant brain tumours
The Gamma Knife procedure poses a lower risk and the process only takes only a day. “The patient can return to normal activities following treatment. The GK can be repeated if required in the future," Dato' Dr Jagdeep said.
According to Dato' Dr Jagdeep, it would be about RM38,000 in most cases. “In vascular cases such as arteriovenous malformation (AVM) where the patient will require an angiogram, the cost will be higher,” he added. The GK is jointly performed by a neurosurgeon and an oncologist and is covered by insurance.

Wait a minute

Wait a minute